Theme: Endeavor the Emerging Issues in Climate Change & Medical Entomology
Climate Change Conference 2019
- About Climate Change and Medical Entomology Conference
- Scientific Sessions
- Market Analysis Report
- News and Updates
CLIMATE CHANGE CONFERENCE 2019
ME Conferences cordially invite you to attend the 8th International Conference on Climate Change and Medical Entomology slated on December 16-17, 2019 at Dubai, UAE . We welcome all scientists, scholars, students, industrialists to attend and explore their knowledge in the field of Climate Change and Medical Entomology.
Climate Change 2019 conference will focus on the latest and exciting innovations in all areas of Climate Change and Medical Entomology which offers a unique opportunity for investigators across the globe to meet, network, and witness new challenges. This year’s annual congress highlights the theme, “Endeavor the Emerging Issues in Climate Change & Medical Entomology” which reflects the Cutting-edge Information. The two days conference includes workshops, symposiums, special keynote sessions conducted by eminent and renowned speakers. This Conference also encourages the active participation of young student researchers as we are hosting Poster Award Competition and Young research Forum at the conference venue.
Benefits of attending Climate Change Conference:
- Build Strategic Business Connections
- Gain New Insights
- Collaborate with the leaders in the fields of Climate Change
- Networking events
- Strategy exchange sessions
- Specialty Exhibit Areas- Companies often have tools to display that we haven’t seen yet
- The focus and energy of Like-Minded Individuals
- The Serendipity of the Random Workshops
- Lightning Sessions
- Market Debuts
Who Attends?
- Climatologist
- Medical Entomologist
- Meteorologist
- Geologist
- Environmental researchers
- Hydrologist
- Marine biologist
- Oceanographer
- Ecologists
- Chemical researchers
- Environmental engineers
- Waste management researchers
- Business entrepreneur
- Astronomers
- Earth science association
- Sustainability Strategists
- CEO’s
- Young research forum
Tracks / Highlights in Climate Change Conference 2019
Track 1: Climate Change and Climatology
Climate change is defined as a change in the statistical distribution of weather patterns. Climatology is the study of the Earth's weather patterns and the systems that cause them.
Climatology is deductively characterized as climate conditions arrived at the midpoint of over a time of time.
Factors such as Biotic processes, variations in solar radiation received by Earth, Plate tectonics, and Volcanic eruptions cause the changes in the Climate. Climatologists today are putting their all efforts towards understanding, explaining and attempting to do something about global warming. Climate Change has become much more prominent nationally and internationally as it is clear that human actions are damaging the environment. Climatology has an exciting future of new discoveries and new technologies. It also has some new challenges to rise as we head deeper into the 21st century.
-
Greenhouse gas emissions
-
Global temperature measurements
-
Changes in precipitation patterns
-
Global ice measurements
-
Natural Climate Drivers
-
Human Impacts on Climate
Track 2: Medical Entomology
Medical entomology is focused upon insects and arthropods that impact human health. Many animal diseases can "jump species" and become a human health threat so Veterinary entomology is also included in this category. Medical entomology also includes scientific research on the behavior, ecology, and epidemiology of arthropod disease vectors, and involves a tremendous outreach to the public in the interest of public safety.
Medical Entomology, in other words, is medical science directly concerned with vectors that affect human and animal health.
-
Veterinary Entomology
-
Biology of Arthropods
-
Importance of Arthropods in Parasitology
-
Medical conditions related to arthropods
-
Vector control measures
-
Parasitology
Track 3: Causes and Effects of Climate Change
There could be several causes for climate change. Rising concentration of carbon dioxide is the factor for climate change that we face today. Some human activities have also been identified as the primary causes of ongoing climate change, often referred to as global warming. Climate change is any significant long-term change of average weather of a region over a significant period of time. The potential future effects of global climate change include more frequent wildfires, longer periods of drought in some regions and an increase in the number, duration and intensity of tropical storms. Taken as a whole, the net damage costs of climate change are likely to be significant and to increase over time.
-
Frost-free season
-
Droughts and heat waves
-
Hurricanes
-
Frequent wildfires
-
Global warming
Track 4: Vector-Borne Diseases
Vector-Borne diseases are caused by parasites, viruses and bacteria that are transmitted by mosquitoes, sand flies, triatomine bugs, black flies, ticks, tsetse flies, mites, snails and lice. Of all infectious diseases, vector-borne diseases account for around 17%. Infected arthropod species bite transmits vector-borne diseases.
Climate is only one of many factors influencing vector distribution and some factors such as habitat destruction, land use, pesticide application, and host density also contributes to Vector-borne Diseases. At present bite of infected mosquitoes, ticks and fleas have more than tripled.
The ecology of Vector-Borne Diseases is complex. In the tropical and sub-tropical regions of developing countries, Insect-borne diseases are mainly found.
-
Dengue fever
-
West Nile Virus
-
Lyme disease
-
Malaria
-
Tick-borne diseases
-
Exotic vector-borne diseases
Track 5: Climate Change and Health
The physical, social and psychological health of humans is affected directly and indirectly by environmental consequences of climate change, such as extreme heat waves, rising sea levels, changes in precipitation resulting in flooding and droughts, intense hurricanes, and degraded air quality etc. Every human is vulnerable to the health impacts associated with climate change. Changes in climate and climate variability particularly changes in weather extremes, affect Climate change, together with other natural and human-made health stressors, influences human health and disease in numerous ways. More people will likely be exposed to the effects of climate change in the next century even greater impacts in the future. People's health is already being harmed by climate change, and the magnitude of this harm is almost certain to get much worse if effective actions are not taken properly.
-
Human Health and Wellbeing Climate
-
Effects of global warming on human health
-
Impact of climate change on health
-
Environmental Conservation
-
Climate Change Health Risks
Track 6: Food Insecurity & Climate Change
Food security and nutrition are affected by all dimensions of Climate change. Global food security, sustainable development and poverty eradication are the serious threat to Climate change. A world without hunger progress can be potentially interrupted by climate change. A robust and coherent global pattern impacts on crop productivity that could have consequences for food availability. Whole food systems stability may be at risk under climate change because of short-term variability in supply. climate change influences on food security. Due to Climate change's impacts on weather patterns will have adverse effects that will threaten food security. Climate change, which is disrupting weather patterns that farmers rely upon is also raising food insecurity to 821 million people worldwide.
-
Food availability Changes
-
Climate change, agriculture and food security
-
Risk of increased food insecurity
-
Food and Nutrition Security & Climate Change
-
Climate Change and Global Food Systems
Track 7: Climate Change: Marine Life
Many of the marine species are affected by climate change include plankton which forms the basis of marine food chains. From warming waters and ocean acidification, marine life faces challenges. Warming waters alter the latitude and depth which harms certain species. Climate change effects on ocean life and ultimately, human life. Changes to the climate is brought by increasing levels of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, which leads to changes in the oceans, including sea-level rise and ocean acidification, which will end up at risk for marine ecosystems and coastal communities. Oxygen levels in the deep ocean have reduced by warming, threatening marine life around the world.
-
Biological diversity on Earth
-
Effects of global warming on oceans
-
Marine protected areas
-
Ocean species and ecosystems
Track 8: Pollution and Climate Changes
Pollution and climate change are closely related. The main sources of CO2 emissions are the extraction and burning of fossil fuels. Climate change and pollution are linked to one another by our increasing use of fossil fuels, including coal, petroleum, and natural gas. According to the WHO, air pollution is closely associated with climate change and in particular, with global warming. Climate change might also affect human health by making our air less healthy to breathe. Drastic changes can lead to an increase in allergens and harmful air pollutants. Air pollution affects people of all ages and across all social classes throughout the world
-
Environment Pollution and Climate Change
-
Urban air pollution and climate change
-
Plastic and Climate Change
-
Harmful air pollutants
-
Marine pollution
-
Air Quality and Climate Change
-
Forest fires
Track 9: Climate Change Challenges & Sustainability
One of the most important global environmental challenges is Climate change, with implications for food production, water supply, health, energy, etc. Climate change is considered to be the most significant challenge to achieving sustainable development, and it threatens to drag millions of people into grinding poverty. Although we are leading better lives than a decade ago, persistent poverty and hunger, as well as rapid urbanization, are challenging. Global emissions of greenhouse gases are rising. This is clearly not sustainable. But scientific knowledge about climate change is advancing rapidly which is a positive note
-
Sustainable Agriculture and Climate Change
-
Climate change, ethics and sustainability
-
Sustainable Development & Climate Change
-
Global Warming, Climate Change and Sustainability
Track 10: Global Warming and Consequences
Increase in temperatures, sea levels rising, and more frequent and intense extreme weather events are causing due to Global warming. Environmental and social changes caused by human emissions of greenhouse gases are the effects of global warming. Far-reaching, long-lasting and in many cases, devastating is expected to the consequences of global warming. There is an increase in average air temperatures near the surface of Earth over the past one to two centuries. Climate change affects all regions around the world. Sea levels are also rising due to the melting of Polar ice shields. The most evident effect of climate change can be clearly seen in the increased temperatures
-
Effects of global warming
-
Impacts of global warming
-
Global Warming Causes, Effects and Solutions
-
Consequences of Global Warming on Human Health
-
Species extinction
Track 11: Oceanography and Marine Biology
Oceanography undertakes extensive research in ocean sciences with a particular focus on the key ocean processes that affect the climate system. The last 4.5 Billion years the Earth's Climate is not static but has evolved over and continues to do so into the Anthropocene. Climate on the Earth is controlled by the interactions among atmosphere, ocean, and land surface. Temperatures rising can also directly affect the metabolism, life cycle, and behavior of marine species. Many marine species could get affected by climate change which alters the metabolism, life cycle, and behavior. Climate change will alter marine life and there is no doubt on it.
-
Physical Oceanography
-
Marine problems: climate change
-
Climate Change on Marine Organisms
Track 12: Ecosystems and biodiversity
Climate change affects the living world through changes in ecosystems and biodiversity. Ecosystems diversity deals with the variations in ecosystems within a geographical location as well as the non-living things with which they interact, such as air, soil, water, and sunlight. Ecosystems bring vital services to society such as biodiversity conservation, protection and enrichment of soils, purification of water and air and reduction of natural disaster risks. Biodiversity is the variability among living organisms including terrestrial, marine, and other aquatic ecosystems and the ecological complexes.
-
Biodiversity and Ecosystem Stability
-
Economics of Ecosystems and Biodiversity
-
The Economics of Ecosystems and Biodiversity
-
Biodiversity in the Forest's Ecosystems
Track 13: Sustainable environment and health
Critical component of sustainable development is protecting and creating healthy environments. Sustainable health can be integrated into Environmental health as a prerequisite for sustainable development. Very little information exists on environmental health and their effects of climate change, pollution and other environmental factors that can-do harm people's health, livelihoods and lives. The longstanding link between the environment and health have led to a recognition of the need for sustainable development. Environmental sustainability is the rates of renewable resource harvest, pollution creation that can be continued indefinitely. It is furthermore defined as responsible interaction with the environment to avoid depletion or degradation of natural resources and allow for long-term environmental quality. To tackle the Earth’s problems, we have to commit ourselves to protect the world natural heritage
-
Sustainable Healthcare
-
Environmental Sustainability
-
Advance Sustainability and the Environment
-
Top Environmental Problems
-
Sustainable Diets
-
Sustainable Environment Research
Track 14: Weather forecasts and scenarios
Weather forecasting is the application of science and technology to predict the state of the weather in an area with an assessment of atmospheric conditions for a given location and time. As much data as possible about the current state of the Temperature, humidity and wind are particularly collected for Weather forecasts. The forecast should reflect different possible uncertainty scenarios associated with every forecast. Climate scenarios are represented by the statistical behavior of the weather based on assumptions. Now excellent information about forecast uncertainty is provided by Computer models
-
Weather forecasting
-
Probability of precipitation forecast
-
Weather Forecasting and Its Classification
-
Weather Analysis and Forecasting
Track 15: Renewable Energy and Resources
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources, which are naturally replenished. These resources are often also referred to as alternative or renewable energy. This includes sunlight, geothermal heat, wind, tides, water, and different types of biomass. This Energy can't be deplenished and is constantly recharged. Solar wind power is an alternative approach to producing clean, non-polluting energy and is considered as most generous renewable energy sources. Ocean waters create a vast store of kinetic energy. Ocean energy has the potential of providing a huge amount of renewable energy around the world.
-
Benefits of Renewable Energy Use
-
Sources of Renewable Energy
-
Solar & Wind Energy
-
Marine Energy
-
Green Energy and Economy
-
Geothermal Energy
Track 16: Biofuels and Bioenergy
Bioenergy and biofuels are recognized globally as crucial elements in the reduction of greenhouse gases for the acceleration of global warming and climate change. Bioenergy is renewable energy made from materials acquired from biological origin. Biomass is any organic matter which has deposited sunlight in the form of chemical energy. In its most exclusive sense, it is a synonym to biofuel, which is fuel obtained from biological sources. This is a common misbelief, as bioenergy is the energy cultivated from the biomass, as the biomass is the fuel and the bioenergy is the energy stored in the fuel.
-
Biomass
-
Algae Biofuels
-
Biodiesel
-
Biomass feedstocks for renewable energy generation
-
Biomass Technologies
-
Production of Biofuels
Track 17: Human Ecology and Social Change
Human ecology is an interdisciplinary study of the relationship between living organisms and humans with their natural, social, and built environments. The ecosystem is considered perceived in human ecology. Human Ecology combines the ideas and methods from several disciplines, including anthropology, sociology, biology, economic history and archaeology. Nature, speed and process of social change in societies always influence nature. Ecosystem functioning reflects the life activities of plants, animals, and microbes and these activities effects feeding, growing, moving, excreting waste, etc.
-
Human ecology and its applications
-
Biotic
-
Abiotic
-
Anthropology
-
Prospects and future directions
Track 18: Nuclear Energy and Technologies
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions that release nuclear energy to generate heat. Nuclear energy comes from splitting atoms in a reactor to heat water into steam, turn a turbine and generate electricity. Nuclear energy provides access to clean, reliable and affordable energy. The effect of nuclear is seen in every organism of the environment from bacteria to plant and to human beings. The damage it causes depends on the level of radiation and the resiliency of the organism. Radiation causes molecules to lose electrons thus destroying it. High doses of radiation can be devastating to the environment.
-
Nuclear Reactions
-
Nuclear Materials
-
Nuclear Radiation
-
Nuclear Medicine
-
Effect of Nuclear Energy
-
Human health
-
Applications of Nuclear Energy
-
Recent Trends in Nuclear Energy
Track 19: Green House Gases and Its Effects
CO2 and other greenhouse gases act like a blanket, absorbing IR radiation and preventing it from escaping into outer space. The net effect is the gradual heating of the Earth's atmosphere and surface, a process known as global warming. A greenhouse gas is a gas that absorbs and emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range. The primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide and ozone. Certain gases in the atmosphere block heat from escaping. Gases in the atmosphere such as carbon dioxide do what the roof of a greenhouse does. The greenhouse effect of Earth's atmosphere keeps some of the Sun's energy from escaping back into space at night.
-
Current trends in global greenhouse gas emissions
-
global emissions
-
Carbon dioxide
-
fossil fuels
-
Solar radiation spectrum
Track 20: Thermal Pollution
Thermal pollution is the degradation of water quality by any process that changes ambient water temperature. A common cause of thermal pollution is the use of water as a coolant by power plants and industrial manufacturers. Many human and natural factors contribute to the problem of thermal pollution. The single biggest cause of thermal pollution is probably cooling for industrial machinery and power plants. Thermal pollution also has some natural causes.
-
Causes and Effects of Thermal Pollution
-
Thermal Pollution of Water
-
Physical effects of thermal pollution
-
Thermal pollution from coal plants
-
Thermal pollution of the atmosphere
Track 21: Climate Change Policies and law
Solving our climate change problems is the moral, economic, policy, political and technological challenge of our generation. This pollution is generated primarily by our region’s heavy concentration of old, highly polluting coal plants. But we can also be a fulcrum for solutions that make good economic and environmental sense. Clean renewable energy and energy efficiency policies, clean air implementation and enforcement, and clean transportation innovation. The shading reflects the number of relevant policies or pieces of legislation in each country. There are more than 1,500 climate laws and policies worldwide
-
Environment and climate change
-
Climate Change Legislation
-
Local Climate Change Law
-
Climate Change Action Plan
Track 22: Control Climate Change
The enormity of global warming can be daunting and dispiriting. Not all are right for everybody. Some you may already be doing or absolutely abhor. But implementing just a few of them could make a difference. Replacing fossil fuels may prove the great challenge of the 21st century. Reducing greenhouse gases is a potential last resort for addressing the challenge of climate change. Purchasing energy-efficient gadgets can also save both energy and money and thus prevent more greenhouse gas emissions.
-
Solutions to Climate Changes
-
Climate change mitigation
-
Climate Change: The Public Health Response
-
Global Climate Change Control
-
Forego Fossil Fuels
-
Future Fuels
Market Growth of Climate Change & Medical Entomology
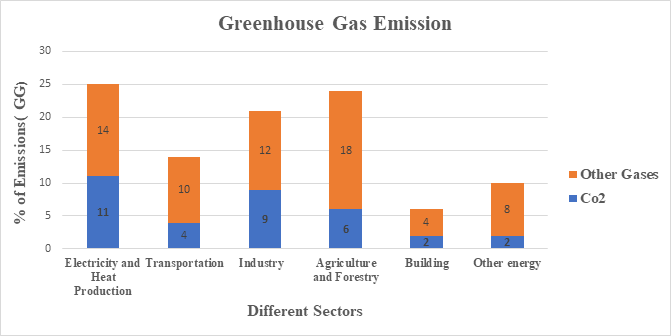
Greenhouse Gas Emission :
One of the most challenging studies nowadays is understanding and interpreting the Changing climate system of the earth. Due to the change in the Climatic Conditions, high Biodiversification and a reduction in Biodiversity is observed. The influence by the humans against the natural forces creates a drastic change by increasing the emission of greenhouse gases which effects not only on particular ecosystem but on a whole planet by industrialization and by desertification increasing levels.
This not only affects the resources but also affects the comfortability of living including shifting shorelines, declining agricultural productivity, the crisis of food supply, availability of water, the health of populations, and flooding, drought, Intense hurricanes which are considered as extreme weather events. Hence there should be in a need of understanding risks, managing them.
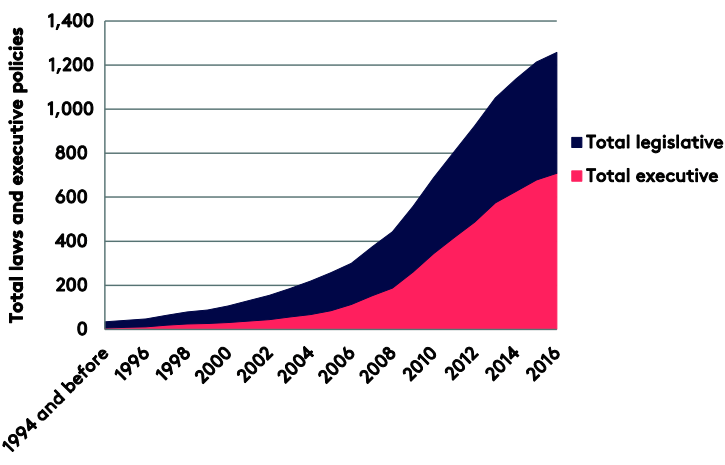
Climate change laws around the world:
There has been a 20-fold increase in the number of global climate change laws since 1997, there were just 60 laws in place with having risen 20-fold to reach 1,260 today which is shown in the database.
The database, produced by the Grantham Research Institute on Climate Change and the Environment and the Sabin Center on Climate Change Law, includes more than 1,200 relevant policies across 164 countries, which account for 95% of global greenhouse gas emissions.
The database shows the extent to which climate change legislation has permeated global political discourse, as well as variations in approach between developed and developing countries.
The stock of climate laws has doubled every four or five years. the number of climate laws continues to grow rapidly. Stepping back from the details, one issue highlighted in the 2017 update report is that current climate policies fall far short of what is needed to avoid global warming of 2oC or more
Related Conferences:
-
9th International Conference on Environment and Climate Change, November 18th-19th, 2019 Johannesburg
-
7th World Congress and Expo on Green Energy, June 24-25, 2019 Barcelona, Spain.
-
8th International Conference on Environment and Climate Change, November 22-23, 2019 Bucharest, Romania.
-
2nd World Conference on Soil Microbiology, Ecology and Biochemistry, February 25-26, 2019 London, UK
-
5th International Conference on Pollution Control & Sustainable Environment, March 14-16, 2019 London, UK.
-
International Conference On Green Energy, April 01-02, 2019 Amsterdam Netherlands.
-
2nd Annual Congress on Soil and Water Sciences, October 22-23, 2019 Berlin, Germany
-
5th International Conference on GIsS and Remote Sensing, September 19-20, 2019 Rome, Italy
-
14th International Conference on Agriculture & Horticulture, August 15-16, 2019 Rome, Italy
Related Universities:
Climate Change and Medical Entomology based Universities in Europe
- University of Oxford
- University of Cambridge
- Delft University of Technology
- Ecol Polytechnique Fédérale de
- Stockholm University
- Technical University of Denmark
- Lund University
- UCL(University College London)
- Aarhus University
- Lancaster University
- RWTH Aachen University
- University of Aberdeen
- University of Birmingham
- University of Bristol
- The University of Exeter
- Ghent University
- University of Helsinki
- University of Leeds
- University of Reading
- University of Southampton
- Uppsala University
- Utrecht University
- Radboud University
- Norwegian University of Science And Technology
- Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences
- Universidad Autónoma de Madrid
- Universität Bremen Albert-Ludwigs-Universitaet Freiburg
- University of Vienna
- Université Pierre et Marie Curie
- University of Liverpool
- Plymouth University
- Aalborg University
- Charles University
- Christian-Albrechts-University zu Kie
- Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen
- Loughborough University
- Queen's University Belfas
- Lomonosov Moscow State University
- Cranfield University
- Cardiff University
- Bangor University
- University of Zurich
Climate Change and Global Warming based Universities in Asia
- National University of Singapore (NUS)
- Tsinghua University
- The University of Tokyo Peking University
- Seoul National University
- National Taiwan University (NTU)
- Kyoto University
- Universiti Sains Malaysia (USM)
- Shanghai Jiao Tong University
- KAIST - Korea Advanced Institute of Science & Technology
- The University of Hong Kong National Taiwan University
- Sun Yat-sen University
- Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur
- Kasetsart University
- National Tsing Hua University
- Pusan National University
- Sungkyunkwan
- University King Abdullah
- Taiwan University of Science and Technology
- Hong Kong Baptist University
- Dalian University of Technology
- China Agricultural University
- Kebangsaan Malaysia University
- University of Tsukuba
- Osaka University
- Kyushu University
- Indian Institute of Technology Bombay
- Indian Institute of Science Asian Institute of Technology
- University of Science and Technology of China
- University Teknologi
- Malaysia University
- Putra Malaysia Tokyo Institute of Technology
- Tohoku University
- Pohang University of Science And Technology
- National Cheng Kung University Korea University
- Hokkaido University Hanyang University
- Fudan University
- Chulalongkorn University
- Beijing Normal University
- The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology
- Shanghai Jiao Tong University
- Kyoto University
- Yale University
- University of California
- The University of Queensland
Climate Change and Medical Entomology based Universities in USA
- University of California-Berkeley
- Stanford University
- Bren School of Environmental Science & Management
- State University of New York College of Environmental Science and Forestry
- Huxley College of the Environment
- University of Michigan
- University of California, Davis
- Yale University
- University of Wisconsin-Madison
- University of Colorado Boulder
- Columbia University
- Johns Hopkins University
- Princeton University
- University of California, Los Angeles
- McGill University
- Arizona State University
- University of Washington
- University of California-Irvine
- University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
- University of Minnesota-Duluth
- Texas A & M University-College Station
- University of Minnesota
- University of Florida
- California State University
- Appalachian State University
- Iowa State University
- Dominican University
- University of Texas
- Saint Cloud State University
- Michigan Technological University
- University of Massachusetts
- University of North Texas
- University of Montana Missoula
- University of Nebraska-Lincoln
- University of Ottawa
- Brown University
- Dalhousie University
- University du Québec
- University of Delaware
- University of Southern California
- Florida State University
- Laval University
- McMaster University
- University of Hawai'i at Mania
- Texas A&M University
- Pennsylvania State University
- University of Missouri, Columbia
- University of New Mexico
- University of Oklahoma
Climate Change and Medical Entomology based Universities in Africa
- University of Oklahoma
- Stellenbosch University
- Rhodes University
- University of Pretoria
- University of the Western Cape
Related Associations:
EUROPEAN SOCIETIES
- Association for Environment Conscious Building
- Centre for Alternative Technology (CAT)
- Climate Action Network - Europe (CAN-Europe)
- Earth Liberation Front (ELF)
- Earth Liberation Prisoner Support Network (ELPSN)
- Environmental Investigation Agency
- Environmental Justice Foundation
- Environmental Law Foundation (ELF)
- Environmental Protection UK
- European Association of Environmental and Resource Economists
- European Biomass Association
- European Environmental Bureau
- Forest Peoples Programme
- Friends of Nature
- Friends of the Earth
- Global Footprint Network
- Global Witness
- Great Transition Initiative
- Green Actors of West Africa (GAWA)
- Green Alliance
- Green Cross International
- Greenpeace
- Groundwork UK
- IDEAS For Us
- International Analog Forestry Network
- International Network for Sustainable Energy(INFORSE)
- International Tree Foundation
- International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN)
- John Muir Trust
- Marine Conservation Society
- National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty
- People & Planet
- Population Matters
- Sandbag
- Scottish Wildlife Trust
- Stop Climate Chaos
- The Civic Trust
- The Corner House
- The Facilities Society (sustainable facilities)
- The Institution of Environmental Sciences
- Town and Country Planning Association
- UK Environmental Law Association (UKELA)
- Whale and Dolphin Conservation Society
- Wildfowl & Wetlands Trust
- Woodland Trust
ASIAN SOCIETIES
- Agency for Non-conventional Energy and Rural Technology (ANERT)
- Australian Conservation Foundation
- Australian Koala Foundation
- Australian Network of Environmental Defenders Offices
- Australian Student Environment Network
- Australian Wildlife Conservancy
- Australian Youth Climate Coalition
- AVAHAN (A Vedic Organization For Humanity And Nature)
- Blue Wedges
- Bombay Natural History Society (BNHS)
- Bush Heritage Australia
- Cape Town Ecology Group
- Centre for Science and Environment (CSE)
- CERES Community Environment Park
- Clean Ocean Foundation
- Delhi Greens (NGO)
- Dolphin Action & Protection Group
- Earthlife Africa
- Emirates Environmental Group
- Endangered Wildlife Trust
- Environment Victoria
- Environmentalist Foundation of India
- EThekwini ECOPEACE
- Foundation for National Parks & Wildlife
- Friends of Nature (China)
- Green Camel Bell
- Greening Australia
- Greenpeace East Asia
- Greenpeace Southeast Asia
- Groundwork
- Himalayan Welfare Organization, Pahalgam
- Keep Australia Beautiful
- Koeberg Alert
- Natural Justice: Lawyers for Communities and the Environment
- PoovulaginNanbargal
- Pragya India
- Saudi Environmental Society
- Sibuyanons Against Mining
- The Earth Organization
- The Wilderness Society (Australia)
- Vindhyan Ecology and Natural History Foundation
- Wildlife & Environment Society
- Wildlife Watch Australia
AMERICAN SOCIETIES
- Alabama Department of Conservation and Natural Resources
- Alabama Department of Environmental Management
- Alaska Department of Environmental Conservation
- Alaska Department of Natural Resources
- Arizona Department of Environmental Quality
- Arizona Game and Fish Department
- Arkansas Department of Environmental Quality
- Australian Koala Foundation
- Australian Network of Environmental Defenders Offices
- Australian Student Environment Network
- Australian Wildlife Conservancy
- Australian Youth Climate Coalition
- California Department of Conservation
- California Department of Fish and Game
- California Department of Forestry and Fire Protection
- California Department of Parks and Recreation
- California Department of Pesticide Regulation
- California Department of Toxic Substances Control
- California Department of Water Resources
- California Environmental Protection Agency
- California Natural Resources Agency
- Colorado Department of Natural Resources
- Connecticut Department of Energy and Environmental Protection
- Delaware Department of Natural Resources and Environmental Control
- Department of Energy and Environment
- Department of Energy and Environment
- Florida Department of Environmental Protection
- Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission
- Illinois Department of Natural Resources
- Indiana Department of Environmental Management
- Iowa Department of Natural Resources
- Kansas Department of Agriculture, Division of Water Resources
- Kansas Department of Health and Environment, Division of Environment
- Kentucky Department for Natural Resources
- Kentucky Department of Environmental Protection
- Louisiana Department of Environmental Quality
- Louisiana Department of Natural Resources
- Maine Department of Environmental Protection
- Maryland Department of Natural Resources
- Maryland Department of the Environment
- Massachusetts Executive Office of Energy and Environmental Affairs (EOEEA)
- Northwest Florida Water Management District
- South Florida Water Management District
- Southwest Florida Water Management District
- St. Johns River Water Management District
- Suwannee River Water Management District
The Truth About West Nile Virus
In most cases, a mosquito-transmitted virus causes West Nile infection. Avoiding mosquito bites is the best method to reduce the risk of infections. Eliminating standing pools of water, such as in old tires, buckets, gutters, and swimming pools can be done to reduce it.
Female mosquito is the prime method of spread of the West Nile virus (WNV). The important mosquito vectors vary according to the area.
- Cats were identified as being hosts for West Nile virus in Europe.
- In the United States, Culex Pipiens is the main vector species.
WNV infected mosquito species feed primarily on birds. Rarely,1 in 150 persons infected with the West Nile virus will develop a more severe form of the disease. Mild disease symptoms will generally last a few days, While Symptoms of the severe disease may last several weeks.
Symptoms
In 80% of infections, people have few or no symptoms.About 20% of people develop symptoms of neurological infections include:
- High fever.
- Vomitings.
- A severe headache.
- Stiff neck.
- Disorientation or confusion.
- Stupor or coma.
- Tremors or muscle jerking.
- Seizures.
- Partial paralysis or muscle weakness.
West Nile virus diagnosis
Besides the physical exam, the presence of the West Nile virus can be confirmed by performing laboratory tests.If you're infected, a blood test may show a rising level of antibodies to the West Nile virus.
West Nile virus treatment
There is no human vaccine. Antiviral treatments for specific West Nile virus infection are available. In some severe cases, patients need to be hospitalized to receive treatment- such as intravenous fluids, pain medication, and nursing care.
West Nile virus prevention
The best way to avoid West Nile virus disease is to prevent mosquito bites: Use insect repellents when you go outdoors. When many mosquitoes are most active wear fully covered proper clothing from dusk through dawn. Install or fix screens on windows and doors.
Conference Highlights
- Climate Change and Climatology
- Medical Entomology
- Causes and Effects of Climate Change
- Vector-Borne Diseases
- Climate Change and Health
- Food Insecurity & Climate Change
- Climate Change: Marine Life
- Pollution and Climate Changes
- Climate Change Challenges & Sustainability
- Global Warming and Consequences
- Oceanography and Marine Biology
- Ecosystems and biodiversity
- Sustainable environment and health
- Weather forecasts and scenarios
- Renewable Energy and Resources
- Biofuels and Bioenergy
- Human Ecology and Social Change
- Nuclear Energy and Technologies
- Green House Gases and Its Effects
- Thermal Pollution
- Climate Change Policies and law
- Control Climate Change
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | December 16-17, 2019 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | |||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Journal of Earth Science & Climatic Change
- Journal of Climatology & Weather Forecasting
- Journal of Pollution Effects & Control
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by



























